Investing in mutual funds is a great way to grow your wealth without the hassle of picking individual stocks. But with so many types of mutual funds available, choosing the right one can be confusing. In this guide, we will explore the different types of mutual funds in detail to help you make informed investment decisions.
Table of Contents
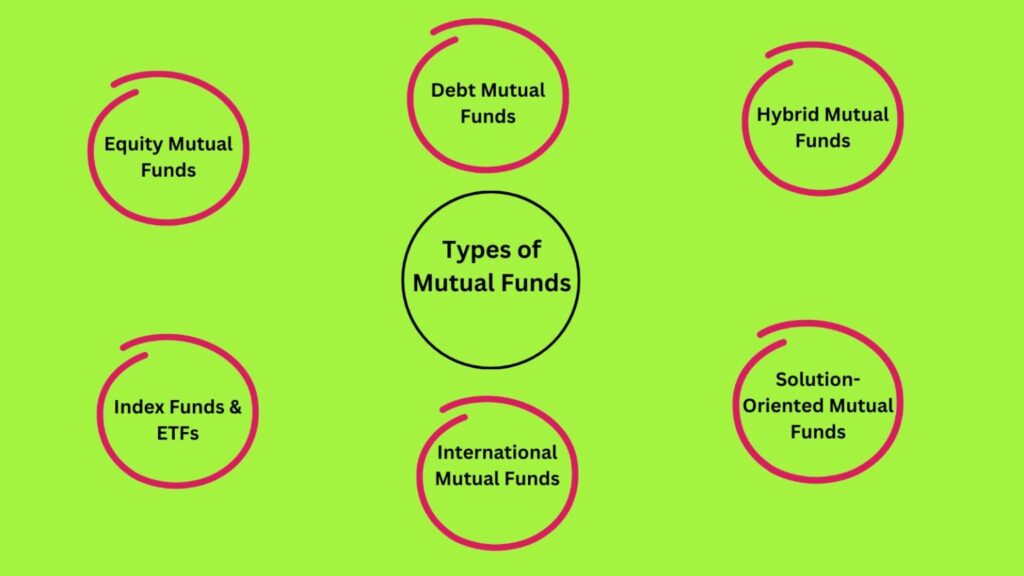
1. Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds invest primarily in stocks, making them ideal for long-term investors looking for higher returns. These funds are further classified into:
- Large-cap Funds: Invest in well-established companies with a strong market presence. These companies are usually industry leaders with stable revenues and profits. Large-cap funds offer relatively lower risk compared to other equity funds.
Example: SBI Blue-chip Fund, ICICI Prudential Blue-chip Fund. - Mid-cap Funds: Target medium-sized companies with growth potential. These companies are in their expansion phase and have the potential to become large-cap companies in the future. They offer higher returns than large-cap funds but also come with higher risk.
Example: DSP Midcap Fund, Kotak Emerging Equity Fund. - Small-cap Funds: Focus on smaller companies with high growth prospects but higher risk. These companies are not yet well-established but have the potential for rapid growth. Due to their volatility, these funds are best suited for aggressive investors.
Example: Nippon India Small Cap Fund, Axis Small Cap Fund. - Sectoral/Thematic Funds: Invest in specific industries like technology, healthcare, or banking. Since these funds are concentrated in one sector, they can be highly rewarding if the sector performs well but also risky if the sector underperforms.
Example: Tata Digital India Fund (Technology), ICICI Prudential Banking and Financial Services Fund (Banking). - ELSS (Equity-Linked Savings Scheme): These types of mutual funds provides tax benefits under Section 80C with a three-year lock-in period. These funds are ideal for investors looking to save taxes while gaining exposure to equity investments.
Example: Aditya Birla Sun Life Tax Relief 96, Axis Long Term Equity Fund. Growth Funds: These funds aim to provide long-term capital appreciation by investing primarily in equities. They are best suited for investors with a high-risk appetite and a long investment horizon. Example: Mirae Asset Large Cap Fund, Axis Blue-chip Fund.
Income Funds:Designed to provide regular income, these funds invest in fixed-income securities such as bonds and debentures. They are ideal for conservative investors looking for stable returns. Example: HDFC Income Fund, ICICI Prudential Regular Savings Fund.
2. Types of Mutual funds based on Debt
Debt mutual funds invest in fixed-income securities like government bonds, corporate bonds, and treasury bills. These are suitable for conservative investors seeking stable returns. Types include:
- Liquid Funds: Invest in short-term debt instruments and offer quick liquidity. These are ideal for parking surplus cash for short periods.
Example: HDFC Liquid Fund, ICICI Prudential Liquid Fund. - Short-term & Long-term Debt Funds: These types of mutual funds cater to different investment horizons with varying interest rate risks. Short-term debt funds invest in bonds with short durations, whereas long-term debt funds invest in long-duration bonds and are more sensitive to interest rate changes.
Example: IDFC Bond Fund (Short-Term), SBI Magnum Income Fund (Long-Term). - Gilt Funds: These types of mutual funds invest only in government securities, making them low-risk investments. Since these funds do not invest in corporate bonds, they carry minimal credit risk.
Example: SBI Magnum Gilt Fund, ICICI Prudential Gilt Fund. - Credit Risk Funds: Invest in lower-rated corporate bonds for higher returns but with added risk. These funds are suitable for investors willing to take on additional risk in exchange for better yields.
Example: DSP Credit Risk Fund, HDFC Credit Risk Debt Fund.
3. Hybrid Mutual Funds
Hybrid funds invest in a mix of equity and debt, providing a balanced approach to risk and return. This types of mutual funds includes:
- Aggressive Hybrid Funds: Have a higher equity allocation, offering better growth potential. These funds are suitable for investors who want exposure to equity with some stability from debt.
Example: ICICI Prudential Equity & Debt Fund, Mirae Asset Hybrid Equity Fund. - Conservative Hybrid Funds: Focus more on debt investments to reduce risk. These funds are ideal for investors looking for steady returns with minimal volatility.
Example: HDFC Hybrid Debt Fund, SBI Debt Hybrid Fund. - Balanced Advantage Funds: Dynamically adjust equity and debt exposure based on market conditions. These funds aim to reduce risks by shifting between asset classes based on market trends.
Example: Edelweiss Balanced Advantage Fund, Motilal Oswal Dynamic Fund.
4. Index Funds & ETFs
These types of mutual funds aim to replicate the performance of a stock market index like the Nifty 50 or Sensex.
- Index Funds: Passively managed funds that track a specific index. These funds are ideal for investors who want to invest in the stock market without active management.
Example: UTI Nifty 50 Index Fund, HDFC Index Sensex Fund. - Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks and offer flexibility. ETFs are similar to index funds but can be bought and sold throughout the trading day. Example: Nippon India ETF Nifty Bees, SBI ETF Sensex
5. Solution-Oriented Mutual Funds
These types of mutual funds are designed to meet specific financial goals such as retirement or children’s education. They have a minimum lock-in period to encourage long-term investing.
- Retirement Funds: Help build a retirement corpus over time. These funds usually have an asset allocation that gradually reduces equity exposure as the investor nears retirement.
Example: HDFC Retirement Savings Fund, Tata Retirement Savings Fund. - Children’s Funds: Focus on securing a child’s future education or other needs. These funds ensure disciplined savings for a child’s future financial requirements.
Example: UTI Children’s Career Fund, ICICI Prudential Child Care Fund.
6. International Mutual Funds
These types of mutual funds invest in stocks and bonds of foreign markets, giving investors exposure to global opportunities. They carry currency exchange risks but can diversify an investment portfolio. International funds allow investors to benefit from the growth of economies outside their home country.
Example: Franklin India Feeder US Opportunities Fund, Motilal Oswal Nasdaq 100 Fund.
Conclusion
Choosing the right mutual fund depends on your financial goals, risk appetite, and investment horizon. Equity funds offer higher returns with risk, debt funds provide stability, hybrid funds balance risk and reward, while index funds and ETFs offer passive investing options. Solution-oriented funds help meet long-term financial goals, and international funds provide exposure to global markets. Before investing, always research the different types of mutual funds performance and consult a financial advisor if needed.
Disclaimer
The content on this platform is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered financial, investment, or legal advice. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we do not guarantee the completeness, reliability, or suitability of the information provided.